What Causes Hypofluorescence?
Pattern #1: Blocked Fluorescence
Reduced visibility of underlying retinal or choroidal circulation due to a barrier located anterior to that circulation. The blocking material should become apparent when comparing the IVFA scan with a colour or red-free photo.
What are causes of blocked retinal fluorescence?
Anterior segment material
Vitreous material
Inner retinal material
What are causes of blocked choroidal fluorescence?
Subretinal Material
Deep Retinal Material
Material that blocks retinal fluorescence may also subsequently block choroidal fluorescence.
Pattern #2: Filling Defect
-
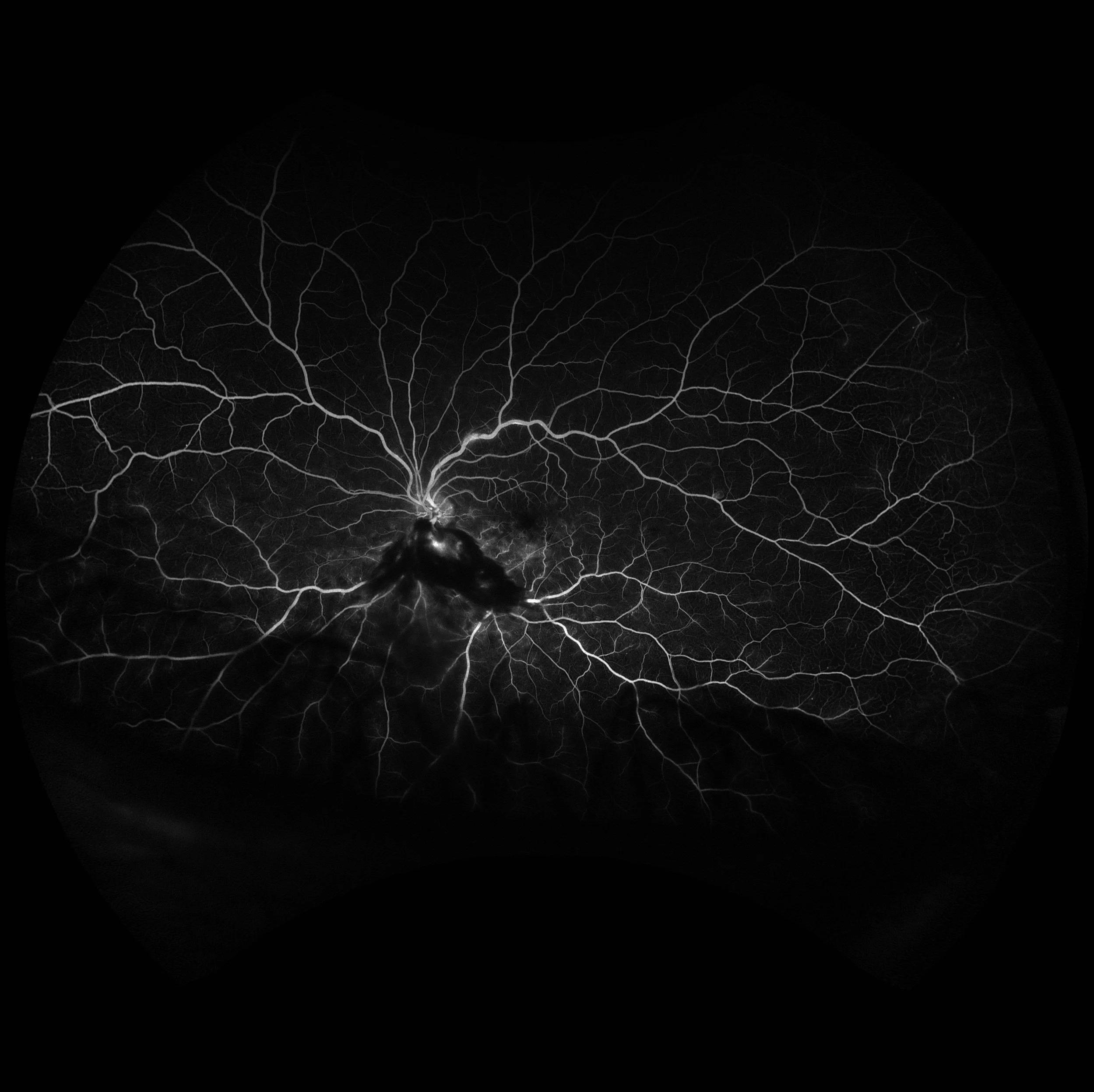
Blocked Fluorescence Due to Vitreous Hemorrhage
Reduced visibility of underlying retinal or choroidal circulation due to a barrier located anterior to that circulation.
A filling defect causes hypofluorescence due to reduced perfusion - meaning less fluorescein is reaching the vasculature.
If there is a complete absence of perfusion, the hypofluorescence will persist throughout the whole angiogram. If there is only partially reduced perfusion, there will be delayed filling.
What causes a vascular filling defect in the retina?
Arterial Defect
Venous Defect
Capillary Bed Defect
Combination Defect
What causes a disc vascular filling defect?
Optic pit and coloboma
Vascular occlusion around the optic disc
Optic atrophy
What causes a choroidal vascular filling defect?
Physiological
Posterior ciliary artery obstruction
Carotid obstruction
Absence of choroidal vascular tissue
-
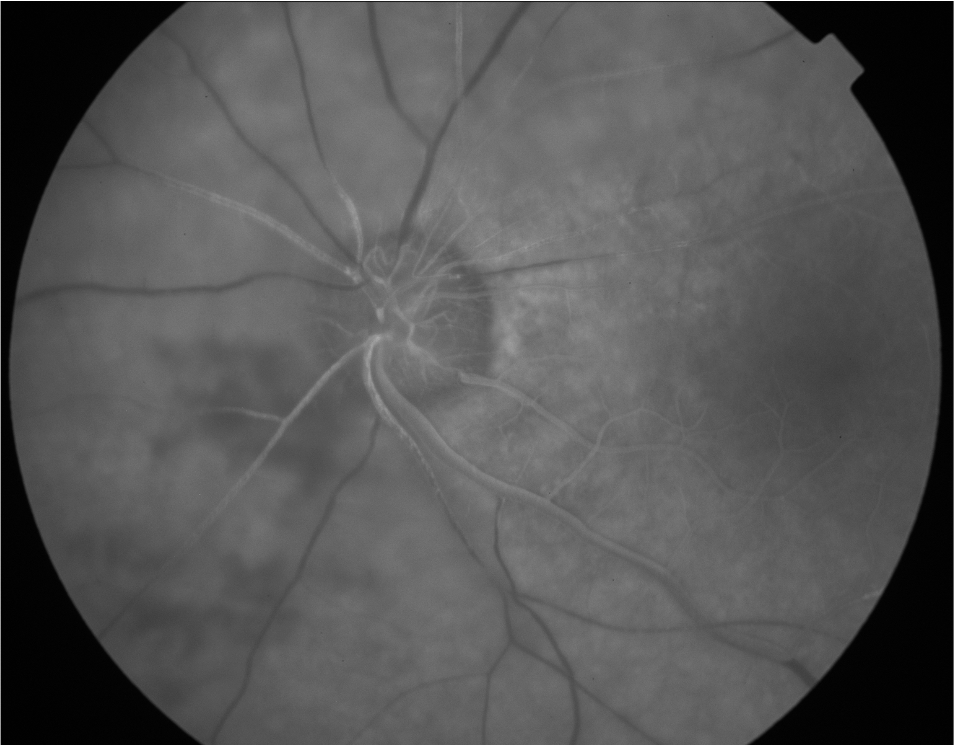
Vascular Filling Defect Due to CRAO
A filling defect causes hypofluorescence due to reduced perfusion - meaning less fluorescein is reaching the vasculature.