Phase 1: The Choroidal Phase (9-15 seconds post-injection)
-
Choroidal filling is seen first due to dye reaching the posterior ciliary artery (PCA) first.
The choroid appears "patchy" due to fenestrations in choriocapillaris, allowing dye to enter the extravascular space.
RPE overlying the choroid results in reduced choroidal fluorescence. Damage in the RPE layer will cause choroidal hyperfluorescence.
Retinal vessels will remain dark in this phase.
10 seconds
Phase 2: The Arterial Phase (1-3 seconds post-choroidal phase)
-
Retinal arteries fluoresce brightly, with peripapillary arteries appearing first.
Retinal vessel endothelium contain tight junctions, preventing dye extravasation unless disease is present.
Background choroidal fluorescence will still be seen
Veins remain dark.
Note: This photo was taken from a different IVFA, with a different vasculature pattern from subsequent photos.
13 seconds
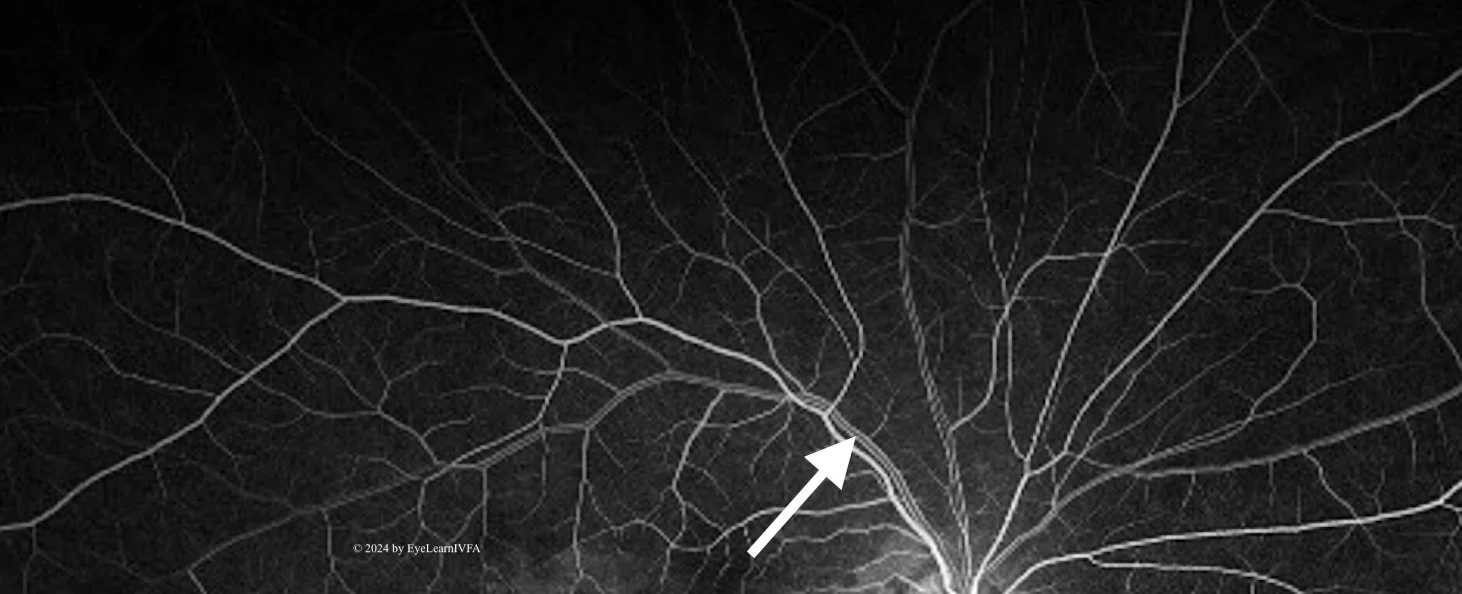
Phase 3: The Early Arteriovenous Phase (1-2 seconds post-arterial phase)
-
Veins begin filling in this phase.
Look for laminar and trilaminar venous flow.
Arrow: Demonstrates Laminar Flow
It occurs when the vein walls appearing more fluorescent than the centre.
Laminar flow occurs due to protein-bound fluorescein being pushed to the vessel periphery, while slower RBCs flow through the centre of the vessel.
At the junction of 2 veins, inner lamina of the veins merge - creating trilaminar flow.
20 seconds
Phase 4: The Late Arteriovenous Phase (20-25 seconds post-injection)
-
Dye completely fills the vein.
Best for visualizing the perifoveal capillary network.
The fovea will to continue to hypofluoresence because of the foveal avascular zone (absence of blood vessels).
The fovea also remains dark because choroidal fluorescence is blocked by increased pigment in the tall macular RPE cells.
25 seconds
Phase 5: The Late Phase (up to 10 minutes post-injection, usually around 5 minutes post-injection)
-
By 10 minutes after injection, the retinal vessels are usually empty.
The disc usually remains hyperfluorescent.
The background has a diffuse fluorescence due to staining of Bruch's membrane, choroid and sclera.
3 min